How to port mirror from multiple physical interfaces (on multiple devices) to a server with single ethernet interface?
(updated 25th March 2013)How to differentiate between port mirroring source? You can choose netflow or sflow for switches, but not all devices can handle as much as every packet - 1:1 packet rate. In my example, I have an SRX 210. Mirrored ports are trunk ports with native vlan configured. You may know it as hybrid port. Incoming packet with no vlan tag is assigned to particular vlan (vlan 10). Other packet must have particluar vlan tag (vlan 5, vlan 6) that is configured on switch port. I did not tested port mirror on Juniper EX switches but rather Avaya switches 5000 series. Juniper EX port mirror configuration is added.
Configuration of Juniper EX switch for this type of port
# show interfaces
ge-0/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [ 5 6 ];
}
native-vlan-id 10;
}
}
}
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [ 5 6 ];
}
native-vlan-id 10;
}
}
}
Port mirroring of TX and RX traffic on Juniper EX switch
# show ethernet-switching-optionsanalyzer myportmirror {
loss-priority high;
input {
ingress {
interface ge-0/0/20.0;
}
egress {
interface ge-0/0/20.0;
}
}
output {
interface {
ge-0/0/0.0;
}
}
}
Avaya ERS 5600 with firmware 6.2.x
port-mirroring mode Xrx monitor-port 1 mirror-port-X 2vlan create 5-6,10 type port 1
vlan configcontrol flexible
vlan members 1 NONE
vlan members 5-6,10 2
vlan ports 2 pvid 10
vlan configcontrol strict
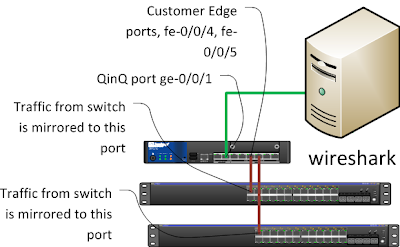
Scenario
We want to mirror traffic from two devices, for example switches, but have server with single interface for pcap.1. Turn on port mirroring on two devices.
2. Connect SRX 210 port ge-0/0/1 to server and ports from that two devices devices to port fe-0/0/4 and fe-0/0/5.
3. Configure 802.1ad (QinQ) on SRX so ge-0/0/1 trunk port is facing a backbone and fe-0/0/4, fe-0/0/5 is facing CE. Each port connected to switch has its own S-vlan. All tagged and untagged (C-vlan) packets will now have additional L2 header (S-vlan).
Diagram
SRX 210 Configuration
interfaces {
ge-0/0/1 {
description "port mirror";
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [ port1 port2 ];
}
}
}
}
description "port mirror";
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode trunk;
vlan {
members [ port1 port2 ];
}
}
}
}
fe-0/0/4 {
description "Mirror 1";
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode access;
vlan {
members port1;
}
}
}
}
fe-0/0/5 {
description "Mirror 2";
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode access;
vlan {
members port2;
}
}
}
}
description "Mirror 1";
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode access;
vlan {
members port1;
}
}
}
}
fe-0/0/5 {
description "Mirror 2";
unit 0 {
family ethernet-switching {
port-mode access;
vlan {
members port2;
}
}
}
}
}
# show vlans
port1 {
vlan-id 1004;
dot1q-tunneling;
}
port2 {
vlan-id 1005;
dot1q-tunneling;
}
To conserve MAC address table on SRX 210, disable MAC address learning on port, or vlans
ethernet-switching-options {
interfaces {
ge-0/0/1.0 {
no-mac-learning;
}
fe-0/0/4.0 {
no-mac-learning;
}
fe-0/0/5.0 {
no-mac-learning;
}
}
}
interfaces {
ge-0/0/1.0 {
no-mac-learning;
}
fe-0/0/4.0 {
no-mac-learning;
}
fe-0/0/5.0 {
no-mac-learning;
}
}
}
I don't see a possibility to create firewall filter that drops incoming packet on port configured with family ethernet-switching.
Observing results. PC with Wireshark is connected to port ge-0/0/1. Please notice text under pictures.
 |
| Packet from fe-0/0/4, tagged to vlan 1004, packet was received untagged on fe-0/0/4. |
 |
| Packet from fe-0/0/4, double tagged with additional vlan 1004, and original vlan 5. |
 |
| Packet from fe-0/0/4, double tagged with additional vlan 1004, and original vlan 6. Difference between this and previous picture is vlan 6. |
Mirrored port fe-0/0/5
 |
| Packet from fe-0/0/5, double tagged with additional vlan 1005, and original vlan 5. |
 |
| Packet from fe-0/0/4, double tagged with additional vlan 1004, and original vlan 5. |
 |
| Packet from fe-0/0/5, double tagged with additional vlan 1004, and original vlan 6. Difference between this and previous picture is vlan 6. |
Note: You can see packets tagged with S-vlan as configured. Each port has its own S-vlan.
Bear in mind that packets received on server could be in wrong order because of SRX internal processing.
Jozef Klacko
References
Application note: J Series and branch SRX series ethernet switching configuration guide (pdf)Avaya support documentation webpage: http://support.avaya.com/downloads/